| Trees
- Giants of the Plant World |



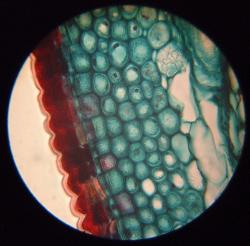
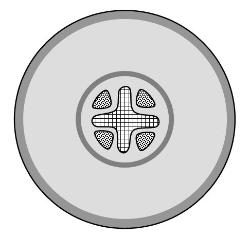
Roots and water transport
Willow (Salix) - a tree of riverbanks the willow is well adapted to wtaer-logged soils.
Sequoiodendron and redwoods - giants among giants!
The
pine tree (Pinus) and the biology
of conifers (cone-bearing trees).
The birch tree (Betula) - a pioneer, easily dispersed, easily takes root where space is found in the woodland but is relatively short-lived for a tree (with a lifespan of about 80 years). May be a dominant tree in birch and aspen woodland in northern highland habitats.
The
beech tree (Fagus) - a large and
shade tolerant tree of well-drained soils, dominant on ideal
habitats, forming beech woodlands with dense canopies that
exclude most competitors.

The yew tree (Taxus) - an extremely long-lived conifer tree native in northern climes. Usually found dispersed among mixed woodland, but dominant in some locales.
dominates mature deciduous woodland on lowland habitats.